
보통 Java에서 정수형을 표현할 때 int형이나 큰 수일경우 long형을 사용합니다. 물론 byte와 short 도 있지만 잘 사용을 하지 않습니다.
| 타입 | 할당되는 메모리의 크기 | 표현 범위 |
| byte | 1 byte | - 128 ~ 127 |
| short | 2 byte | -215 ~ (215 - 1) |
| -32,768 ~ 32,767 | ||
| int |
4 byte | -231 ~ (231 - 1) |
| -2,147,483,648 ~ 2,147,483,647 | ||
| long |
8 byte |
-263 ~ (263 - 1) |
| -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 ~ 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
거의 대부분 long 타입으로 표현할 수 있지만 표현 범위를 넘어서는 아주 큰 수를 표현하기엔 한계가 있습니다.
만약에 표현 범위를 넘어서게 된다면 다음과 같은 에러가 발생합니다.

| 타입 | 할당되는 메모리의 크기 | 표현 범위 | 유효 자릿수 | |
| float | 4 byte | 1.4E-45 ~ 3.4E38 (1.4×10^-45 ~ 3.4×10^38) | 소수점 7번째 까지 유효 | |
| double | 8 byte | 4.9E-324 ~ 1.8E308 (4.9×10^-324 ~ 1.8×10^308) | 소수점 16번째 까지 유효 |
부동 소수점을 이용하여 실수형을 저장할 수 있는 타입에는 float와 double이 있습니다.
그런데 float와 double은 문제점이 있습니다.
바로 소수점 이하의 수를 다룰 때 정확한 값이 아닌 이진수의 근사치를 저장하기 때문입니다.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 100.00000006;
double b = 10.00000005;
System.out.println((a-b) == 90.00000001); // false
}
}
위 코드의 결과는 예상대로라면 true라고 떠야 하지만 결과는 false가 나옵니다. 이러한 결과가 나오는 이유는 위에서 말했듯이 Java는 부동 소수점 방식을 사용하기 때문에 근사치를 저장하기 때문입니다.
이러한 문제점들 때문에 정수형과 실수형을 표현할 때 Java.math 패키지 안에 있는 BigInteger와 BigDecimal 클래스를 사용해야 합니다.
BigInteger란 ❓
BigInteger란 int와 long 타입이 표현할 수 있는 범위보다 훨씬 큰 정수를 표현하기 위한 클래스
import java.math.BigInteger;
BigInteger bigNumber = new BigInteger("123");
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("FFFF", 16);
BigInteger bigInteger = BigInteger.valueOf(1234567);
먼저 BigInteger 클래스를 사용하기 위해서는 BigInteger 패키지는 import 해야 합니다. 위와 같이 문자열, n진수와 valueOf()를 사용하여 정수형도 가능합니다.
BigInteger의 연산
BigInteger 자료형은 클래스 구조이며 인자로 문자열을 받아 동작하기 때문에 기존의 사칙연산(+, -, *, /)을 사용할 수 없습니다.
그렇기 때문에 연산이 필요할 때는 내장 메서드를 사용해야 합니다.
| 메서드 | 설명 |
| BigInteger add(BigInteger val) | 덧셈(this + val) |
| BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) | 뺄셈(this - val) |
| BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) | 곱셈(this * val) |
| BigInteger divide(BigInteger val) | 나눗셈(this / val) |
| BigInteger remainder(BigInteger val) | 나머지(this % val) |
BigInteger bigNumber1 = new BigInteger("12345");
BigInteger bigNumber2 = new BigInteger("6789");
System.out.println("덧셈(+) :" +bigNumber1.add(bigNumber2));
System.out.println("뺄셈(-) :" +bigNumber1.subtract(bigNumber2));
System.out.println("곱셈(*) :" +bigNumber1.multiply(bigNumber2));
System.out.println("나눗셈(/) :" +bigNumber1.divide(bigNumber2));
System.out.println("나머지(%) :" +bigNumber1.remainder(bigNumber2));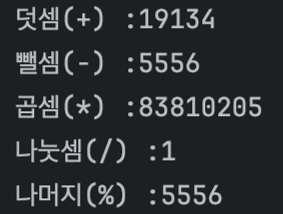
BigInteger 비교
BigInteger의 값을 비교할 때는 compareTo() 메서드를 사용하면 됩니다.
BigInteger bigNumber1 = new BigInteger("100000");
BigInteger bigNumber2 = new BigInteger("1000000");
System.out.println(bigNumber1.compareTo(bigNumber2));
위와 같이 사용하면되고, 반환 값은 두 수를 비교하고 같으면 0 / 다르면 -1 / 더 크면 1이 반환됩니다.
BigInteger 상수표현
System.out.println(new BigInteger("20").add(BigInteger.valueOf(10)));
BigInteger()는 문자열로 동작하기 때문에 위와 같이 캐스팅 작업이 한번 필요합니다.
BigInteger 클래스는 자주 사용되는 숫자인 0,1,2,10에 대해서 상수를 제공합니다.
public class ConstantTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(BigInteger.ZERO); // 0
System.out.println(BigInteger.ONE); // 1
System.out.println(BigInteger.TWO); // 2
System.out.println(BigInteger.TEN); // 10
System.out.println(new BigInteger("20").add(BigInteger.TEN)); // 30
}
}
위와 같이 사용할 수 있으며, 기존의 상수를 쓰는 이유와 같이 가독성과 안정성 더불어 캐스팅 작업을 생략할 수 있기 때문에 편리함까지 있습니다.
BigInteger의 형변환
BigInteger 클래스는 다른 타입으로 변환할 수 있는 캐스팅도 내장 함수를 사용해야 합니다.
public class CastTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger num = new BigInteger.valueOf(1000);
int int_num = num.intValue();
long long_num = long.longValue();
float float_num = num.floatValue();
double double_num = double.doubleValue();
String String_num = num.toString();
}
}
BigDecimal란 ❓
import java.math.BigDecimal;
BigDecimal 클래스는 BigInteger 클래스와 마찬가지로 java.math 패키지 안에 포함되어 있기 때문에 똑같이 import가 필요합니다.
보기에서 알 수 있듯이 BigInteger와 비슷하게 생겼습니다. 사용법도 비슷하며 BigInteger 클래스와 차이점은 BigInteger는 정수 BigDecimal은 실수라고 생각하면 쉽습니다.
import java.math.BigDecimal;
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new bigDecimal("123.456");
BigDecimal bdFromLong = BigDecimal.valueOf(123412345678901L, 2);
char[] c = {'1', '2', '3'};
BigDecimal cd = new BigDecimal(c);
BigDecimal의 변수
public class CastTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal num = new BigDecimal("1234.56789");
System.out.println("intValue : "+ num.intValue());
System.out.println("unscaledValue : " +num.unscaledValue());
System.out.println("scale : " + num.scale());
System.out.println("precision : "+num.precision());
}
}
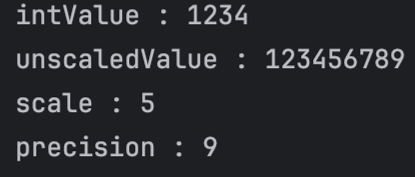
- intValue : 정수.
- 정수를 저장하는데 BigInteger를 사용합니다.
- precision: 숫자를 구성하는
전체 자릿수,왼쪽부터 0이 아닌 수가 시작하는 위치부터 오른쪽부터 0이 아닌 수로 끝나는 위치까지의 총자릿수입니다.- unscale과 동의어
- scale: 지수.
- 전체 소수점 자릿수, 소수점 첫째 자리부터 오른쪽부터 0이 아닌 수로 끝나는 위치까지의 총 소수점 자릿수입니다.
- fraction과 동의어
BigDecimal의 소수점 처리
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("1.000");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("3.000");
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2);
위 코드를 실행하면 다음과 같은 에러가 발생합니다.

이유는 1.0 / 3.0의 결과가 0.333.....으로 계속 되기 때문입니다. 이러한 경우에는 RoundingModed에서 제공하는 메서드를 사용하면 됩니다.
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal, 3, RoundingMode.CELING); //0.334
- CEILING : 올림
- FLOOR : 내림
- UP : 양수일 때는 올림, 음수일 때는 내림
- DOWN : 양수일 때는 내림, 음수일 때는 올림
- HALF_UP : 반올림(5이상 올림, 6 미만 버림)
- HALF_DOWN : 반올림(6이상 올림, 6 미만 버림)
- HALF_EVEN : 반올림(반올림 자리의 값이 짝수면 HALF_DOWN, 홀수면 HALF_UP)
- UNNECESSARY : 나눗셈의 결과가 딱 떨어지는 수가 아니면 ArithmeticException 발생
'Language > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] Stream API에 대해 알아보기 _ Stream 생성 (2/5) (0) | 2024.05.16 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] Stream API에 대해 알아보기 (1/5) (0) | 2024.05.15 |
| [JAVA] char에서 String으로 변환하기 (value of() , charAt()) (0) | 2024.05.12 |
| [JAVA] 입출력, BufferedReader, StringTokenizer, StringBuilder 알아보기 (0) | 2024.05.12 |
| [JAVA] 형 변환 (캐스팅, casting) 알아보기 (0) | 2024.04.29 |

보통 Java에서 정수형을 표현할 때 int형이나 큰 수일경우 long형을 사용합니다. 물론 byte와 short 도 있지만 잘 사용을 하지 않습니다.
| 타입 | 할당되는 메모리의 크기 | 표현 범위 |
| byte | 1 byte | - 128 ~ 127 |
| short | 2 byte | -215 ~ (215 - 1) |
| -32,768 ~ 32,767 | ||
| int |
4 byte | -231 ~ (231 - 1) |
| -2,147,483,648 ~ 2,147,483,647 | ||
| long |
8 byte |
-263 ~ (263 - 1) |
| -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 ~ 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
거의 대부분 long 타입으로 표현할 수 있지만 표현 범위를 넘어서는 아주 큰 수를 표현하기엔 한계가 있습니다.
만약에 표현 범위를 넘어서게 된다면 다음과 같은 에러가 발생합니다.

| 타입 | 할당되는 메모리의 크기 | 표현 범위 | 유효 자릿수 | |
| float | 4 byte | 1.4E-45 ~ 3.4E38 (1.4×10^-45 ~ 3.4×10^38) | 소수점 7번째 까지 유효 | |
| double | 8 byte | 4.9E-324 ~ 1.8E308 (4.9×10^-324 ~ 1.8×10^308) | 소수점 16번째 까지 유효 |
부동 소수점을 이용하여 실수형을 저장할 수 있는 타입에는 float와 double이 있습니다.
그런데 float와 double은 문제점이 있습니다.
바로 소수점 이하의 수를 다룰 때 정확한 값이 아닌 이진수의 근사치를 저장하기 때문입니다.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 100.00000006;
double b = 10.00000005;
System.out.println((a-b) == 90.00000001); // false
}
}
위 코드의 결과는 예상대로라면 true라고 떠야 하지만 결과는 false가 나옵니다. 이러한 결과가 나오는 이유는 위에서 말했듯이 Java는 부동 소수점 방식을 사용하기 때문에 근사치를 저장하기 때문입니다.
이러한 문제점들 때문에 정수형과 실수형을 표현할 때 Java.math 패키지 안에 있는 BigInteger와 BigDecimal 클래스를 사용해야 합니다.
BigInteger란 ❓
BigInteger란 int와 long 타입이 표현할 수 있는 범위보다 훨씬 큰 정수를 표현하기 위한 클래스
import java.math.BigInteger;
BigInteger bigNumber = new BigInteger("123");
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("FFFF", 16);
BigInteger bigInteger = BigInteger.valueOf(1234567);
먼저 BigInteger 클래스를 사용하기 위해서는 BigInteger 패키지는 import 해야 합니다. 위와 같이 문자열, n진수와 valueOf()를 사용하여 정수형도 가능합니다.
BigInteger의 연산
BigInteger 자료형은 클래스 구조이며 인자로 문자열을 받아 동작하기 때문에 기존의 사칙연산(+, -, *, /)을 사용할 수 없습니다.
그렇기 때문에 연산이 필요할 때는 내장 메서드를 사용해야 합니다.
| 메서드 | 설명 |
| BigInteger add(BigInteger val) | 덧셈(this + val) |
| BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val) | 뺄셈(this - val) |
| BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val) | 곱셈(this * val) |
| BigInteger divide(BigInteger val) | 나눗셈(this / val) |
| BigInteger remainder(BigInteger val) | 나머지(this % val) |
BigInteger bigNumber1 = new BigInteger("12345");
BigInteger bigNumber2 = new BigInteger("6789");
System.out.println("덧셈(+) :" +bigNumber1.add(bigNumber2));
System.out.println("뺄셈(-) :" +bigNumber1.subtract(bigNumber2));
System.out.println("곱셈(*) :" +bigNumber1.multiply(bigNumber2));
System.out.println("나눗셈(/) :" +bigNumber1.divide(bigNumber2));
System.out.println("나머지(%) :" +bigNumber1.remainder(bigNumber2));
BigInteger 비교
BigInteger의 값을 비교할 때는 compareTo() 메서드를 사용하면 됩니다.
BigInteger bigNumber1 = new BigInteger("100000");
BigInteger bigNumber2 = new BigInteger("1000000");
System.out.println(bigNumber1.compareTo(bigNumber2));
위와 같이 사용하면되고, 반환 값은 두 수를 비교하고 같으면 0 / 다르면 -1 / 더 크면 1이 반환됩니다.
BigInteger 상수표현
System.out.println(new BigInteger("20").add(BigInteger.valueOf(10)));
BigInteger()는 문자열로 동작하기 때문에 위와 같이 캐스팅 작업이 한번 필요합니다.
BigInteger 클래스는 자주 사용되는 숫자인 0,1,2,10에 대해서 상수를 제공합니다.
public class ConstantTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(BigInteger.ZERO); // 0
System.out.println(BigInteger.ONE); // 1
System.out.println(BigInteger.TWO); // 2
System.out.println(BigInteger.TEN); // 10
System.out.println(new BigInteger("20").add(BigInteger.TEN)); // 30
}
}
위와 같이 사용할 수 있으며, 기존의 상수를 쓰는 이유와 같이 가독성과 안정성 더불어 캐스팅 작업을 생략할 수 있기 때문에 편리함까지 있습니다.
BigInteger의 형변환
BigInteger 클래스는 다른 타입으로 변환할 수 있는 캐스팅도 내장 함수를 사용해야 합니다.
public class CastTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger num = new BigInteger.valueOf(1000);
int int_num = num.intValue();
long long_num = long.longValue();
float float_num = num.floatValue();
double double_num = double.doubleValue();
String String_num = num.toString();
}
}
BigDecimal란 ❓
import java.math.BigDecimal;
BigDecimal 클래스는 BigInteger 클래스와 마찬가지로 java.math 패키지 안에 포함되어 있기 때문에 똑같이 import가 필요합니다.
보기에서 알 수 있듯이 BigInteger와 비슷하게 생겼습니다. 사용법도 비슷하며 BigInteger 클래스와 차이점은 BigInteger는 정수 BigDecimal은 실수라고 생각하면 쉽습니다.
import java.math.BigDecimal;
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new bigDecimal("123.456");
BigDecimal bdFromLong = BigDecimal.valueOf(123412345678901L, 2);
char[] c = {'1', '2', '3'};
BigDecimal cd = new BigDecimal(c);
BigDecimal의 변수
public class CastTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal num = new BigDecimal("1234.56789");
System.out.println("intValue : "+ num.intValue());
System.out.println("unscaledValue : " +num.unscaledValue());
System.out.println("scale : " + num.scale());
System.out.println("precision : "+num.precision());
}
}

- intValue : 정수.
- 정수를 저장하는데 BigInteger를 사용합니다.
- precision: 숫자를 구성하는
전체 자릿수,왼쪽부터 0이 아닌 수가 시작하는 위치부터 오른쪽부터 0이 아닌 수로 끝나는 위치까지의 총자릿수입니다.- unscale과 동의어
- scale: 지수.
- 전체 소수점 자릿수, 소수점 첫째 자리부터 오른쪽부터 0이 아닌 수로 끝나는 위치까지의 총 소수점 자릿수입니다.
- fraction과 동의어
BigDecimal의 소수점 처리
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("1.000");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("3.000");
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal2);
위 코드를 실행하면 다음과 같은 에러가 발생합니다.

이유는 1.0 / 3.0의 결과가 0.333.....으로 계속 되기 때문입니다. 이러한 경우에는 RoundingModed에서 제공하는 메서드를 사용하면 됩니다.
bigDecimal1.divide(bigDecimal, 3, RoundingMode.CELING); //0.334
- CEILING : 올림
- FLOOR : 내림
- UP : 양수일 때는 올림, 음수일 때는 내림
- DOWN : 양수일 때는 내림, 음수일 때는 올림
- HALF_UP : 반올림(5이상 올림, 6 미만 버림)
- HALF_DOWN : 반올림(6이상 올림, 6 미만 버림)
- HALF_EVEN : 반올림(반올림 자리의 값이 짝수면 HALF_DOWN, 홀수면 HALF_UP)
- UNNECESSARY : 나눗셈의 결과가 딱 떨어지는 수가 아니면 ArithmeticException 발생
'Language > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] Stream API에 대해 알아보기 _ Stream 생성 (2/5) (0) | 2024.05.16 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] Stream API에 대해 알아보기 (1/5) (0) | 2024.05.15 |
| [JAVA] char에서 String으로 변환하기 (value of() , charAt()) (0) | 2024.05.12 |
| [JAVA] 입출력, BufferedReader, StringTokenizer, StringBuilder 알아보기 (0) | 2024.05.12 |
| [JAVA] 형 변환 (캐스팅, casting) 알아보기 (0) | 2024.04.29 |
